St. Elizabeth's Hospital issued the following announcement on May 17.
Every minute a person’s brain is without oxygen due to a stroke, 2 million brain cells die. This can often lead to brain damage, disability or death.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) identifies stroke as the third-leading cause of death in Illinois, with more than 6,000 deaths annually.
HSHS St. Elizabeth’s Hospital encourages community members to know the most common signs of stroke:
- Sudden dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden numbness of the face, arm or leg
- Sudden trouble seeing
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause
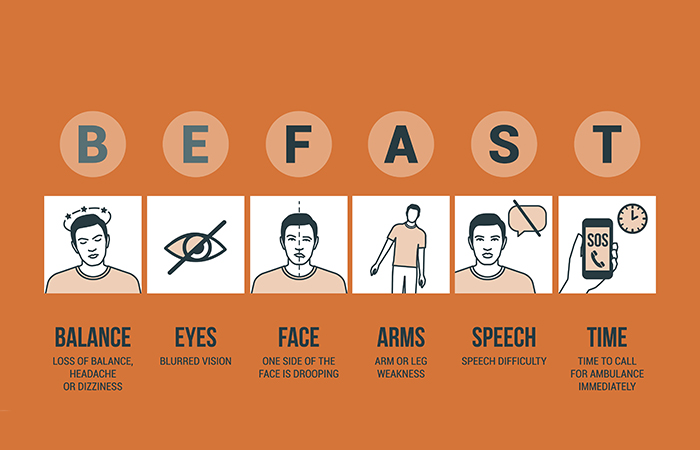
B – Balance: Ask the person to attempt to stand. Is he or she dizzy?
E – Eye changes: Ask the person to look at you. Does he or she report blurred vision?
F – Face drooping: Ask the person to smile. Does one side droop?
A – Arm weakness: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S – Slurred speech: Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Are the words slurred?
T – Time to call 9-1-1: If the person shows any of these signs, call 9-1-1 immediately.
Treatment for stroke can begin in the ambulance so it is important for the public to know the signs and symptoms of a stroke and to get medical assistance as soon as possible. The chances of survival are greater when emergency treatment begins quickly, so patients should ALWAYS call 9-1-1 if a stroke is suspected. Immediate treatment and early intervention may minimize the long-term effects of stroke.
In the United States, the CDC says 800,000 people have a stroke every year, however 80% of strokes are preventable by making lifestyle changes to reduce your risk:
- Don’t smoke
- Be physically active
- Control cholesterol
- Control blood pressure
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Reduce blood sugar
The most common type of stroke is an ischemic stroke, which occurs when blood flow through the artery that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the brain becomes blocked. In the United States, 87% of strokes are ischemic.
A hemorrhagic stroke happens when an artery in the brain leaks blood or ruptures, putting too much pressure on brain cells which damages them.
If you think someone is having a stroke, call 9-1-1 immediately. For more information about signs, symptoms and how to respond, visit the American Stroke Association or the CDC stroke webpage.
Original source can be found here.
Source: St. Elizabeth's Hospital




 Alerts Sign-up
Alerts Sign-up